
Marketing is the backbone of business strategy, crucial for reaching and engaging customers. Over the years, the landscape of marketing has evolved dramatically, primarily due to advancements in technology. This evolution has given rise to two dominant forms of marketing: digital marketing and traditional marketing. While both aim to promote products and services, their methods, reach, and impact differ significantly. This article delves into the intricacies of digital and traditional marketing, comparing their advantages, disadvantages, and effectiveness in the modern business environment.
Understanding Traditional Marketing
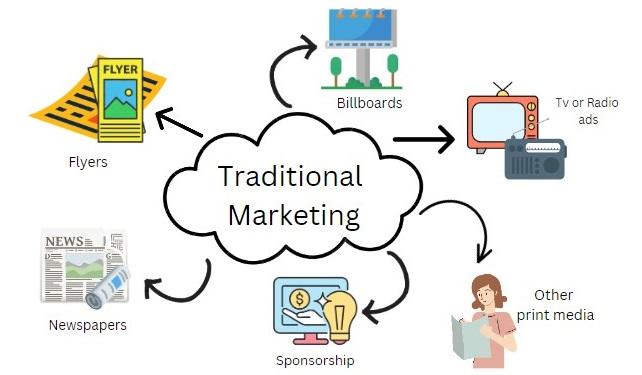
Traditional marketing refers to any marketing strategy that utilizes conventional media channels to promote products and services. This includes:
- Print Media: Newspapers, magazines, brochures, and flyers.
- Broadcast Media: Television and radio advertisements.
- Outdoor Advertising: Billboards, posters, and transit ads.
- Direct Mail: Catalogs and promotional materials sent directly to consumers.
- Telemarketing: Direct phone calls to potential customers.
Traditional marketing primarily relies on mass media to reach a broad audience. Its effectiveness often lies in its ability to build brand awareness and credibility, particularly among older demographics who may be less engaged with digital platforms.

Pros of Traditional Marketing
- Brand Recognition: Traditional marketing can effectively create brand awareness and recognition, especially in local markets.
- Targeting Specific Demographics: Certain traditional methods, such as local newspapers or radio stations, can effectively reach specific demographic groups.
- Tangible Materials: Print advertisements can be physically held and reviewed, which some consumers find more trustworthy.
Cons of Traditional Marketing
- Cost: Traditional marketing can be expensive, particularly for television and radio spots.
- Limited Reach: It often has geographical limitations, making it less effective for global outreach.
- Difficulty in Measurement: Tracking the effectiveness of campaigns can be challenging, as it often relies on indirect metrics like sales increases rather than direct engagement data.
Understanding Digital Marketing

Digital marketing encompasses all marketing efforts that use the internet or electronic devices. This includes:
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Improving website visibility on search engines.
- Social Media Marketing: Utilizing platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter to engage with audiences.
- Email Marketing: Sending targeted messages to consumers via email.
- Content Marketing: Creating valuable content to attract and retain an audience.
- Pay-Per-Click (PPC): Paid advertising on search engines and social media platforms.
Digital marketing is characterized by its ability to reach a global audience, engage users in real-time, and provide measurable results.
Pros of Digital Marketing

- Cost-Effectiveness: Digital marketing is generally less expensive than traditional marketing, allowing for a better return on investment (ROI).
- Targeted Audience Reach: Marketers can target specific audiences based on demographics, interests, and online behavior.
- Measurable Results: Digital marketing provides tools for tracking and analyzing campaign performance in real-time, allowing for quick adjustments.
- Interactivity: Digital platforms facilitate two-way communication between brands and consumers, fostering engagement and feedback.
Cons of Digital Marketing
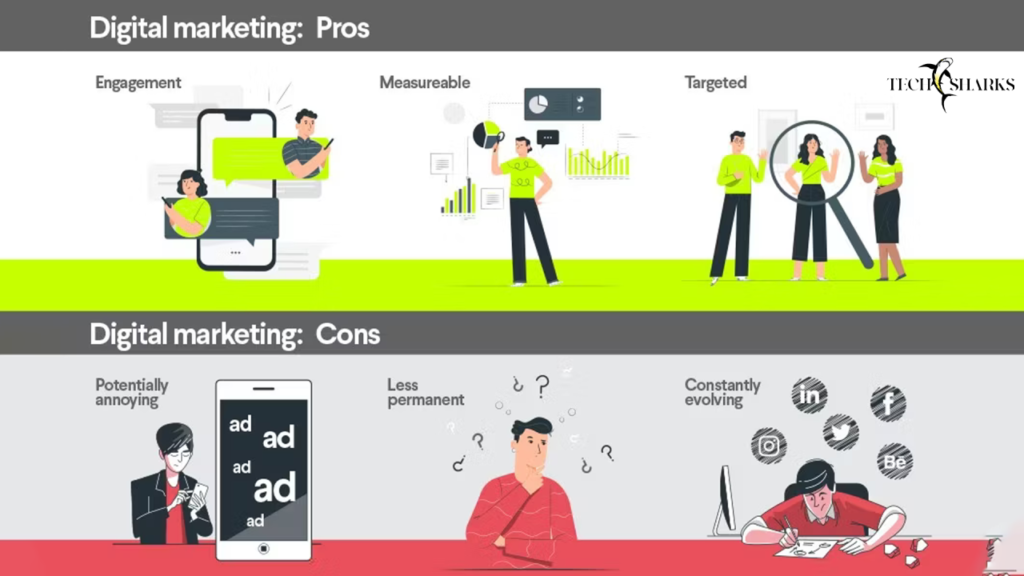
- Over-Saturation: The digital space is crowded, making it challenging for brands to stand out.
- Dependence on Technology: Digital marketing requires a certain level of technological proficiency and access to the internet.
- Privacy Concerns: Consumers are increasingly wary of how their data is used, which can impact engagement.
Comparing Digital and Traditional Marketing
Reach and Audience Targeting
- Digital Marketing:
- Global Reach: Can target audiences worldwide, breaking geographical barriers.
- Precise Targeting: Utilizes data and analytics to target specific demographics, interests, and behaviors. This precision ensures that marketing efforts are directed toward the most relevant audience segments.
- Traditional Marketing:
- Local Reach: Often more effective for local or regional campaigns.
- Broad Targeting: Less precise, relying on general demographics. Advertisers target a broad audience based on the medium’s reach, making it difficult to focus on specific consumer segments.
Cost-Effectiveness
- Digital Marketing:
- Lower Costs: Generally more affordable, especially for small businesses. Platforms like social media and email marketing offer cost-effective ways to reach a large audience.
- Pay-Per-Click: Allows advertisers to control budgets and only pay when users interact with ads.
- Traditional Marketing:
- Higher Costs: Often requires a significant budget, especially for prime-time TV slots or full-page newspaper ads.
- Fixed Costs: Advertisers pay a set fee regardless of audience engagement, which can be costly without guaranteed results.
Case Studies and Examples
Successful Digital Marketing Campaigns
- Nike’s Social Media Campaigns:
- Strategy: Leveraged platforms like Instagram and Twitter to create engaging content, including user-generated posts and influencer collaborations.
- Result: Increased brand loyalty and significant growth in online sales.
- Old Spice’s Viral Video Campaign:
- Strategy: Released humorous and shareable videos on YouTube and social media.
- Result: Dramatically increased brand awareness and sales, reaching a younger demographic.
Successful Traditional Marketing Campaigns
- Coca-Cola’s TV Advertisements:
- Strategy: Iconic TV commercials with memorable jingles and storytelling.
- Result: Reinforced brand image and maintained top-of-mind awareness across generations.
- Marlboro’s Print Advertising:
- Strategy: Created the Marlboro Man campaign in magazines and billboards.
- Result: Transformed the brand’s image, leading to significant market share growth.
The Future of Marketing: Integrating Digital and Traditional
The future of marketing lies in integrating digital and traditional strategies to create a cohesive, omnichannel approach. Businesses can leverage the strengths of both to maximize reach and impact.
Benefits of Integration
- Wider Reach: Combines the broad reach of traditional media with the precision of digital channels.
- Consistent Messaging: Ensures a unified brand message across all platforms.
- Enhanced Engagement: Uses traditional media to drive traffic to digital platforms for further interaction and engagement.
Strategies for Integration
- Cross-Promotion: Use traditional ads to promote digital channels (e.g., TV commercials encouraging viewers to visit a website or follow on social media).
- Unified Campaigns: Develop campaigns that start in traditional media and continue online, creating a seamless experience.
- Data Utilization: Apply insights from digital analytics to refine traditional marketing efforts, ensuring they resonate better with the target audience.
Conclusion
Both digital and traditional marketing have unique strengths and limitations. Digital marketing excels in precision, cost-effectiveness, and real-time engagement, making it indispensable in the modern digital age. Traditional marketing, with its broad reach and impactful presence, remains relevant, especially for brand-building and local campaigns.
The most effective marketing strategies often blend both approaches, leveraging the wide reach of traditional media and the precise targeting capabilities of digital platforms. By understanding the differences and synergies between digital and traditional marketing, businesses can craft comprehensive strategies that drive growth and success in a competitive marketplace.